Unicornuate Uterus – Definition, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Fertility & Treatment
As a Gynecologist and Fertility Expert, I am highly familiar with the complexities of congenital uterine anomalies, and I specialize in addressing the concerns and confusion these conditions raise for women
One of the most common conditions we see in clinical practice is the unicornuate uterus. Let me take you through everything you need to know about the unicornuate uterus so you can make informed decisions about your reproductive health.
What is a Unicornuate Uterus?
A unicornuate uterus is one of the commonest Müllerian duct anomalies, characterized by the presence of only one fully developed uterine horn.
Normally, the uterus develops from two Müllerian ducts that fuse together during fetal development. In this condition, one duct fails to develop properly—either disappearing completely or partially—leaving only one functional side.
This anomaly can exist with or without a rudimentary horn (an underdeveloped piece of uterine tissue).
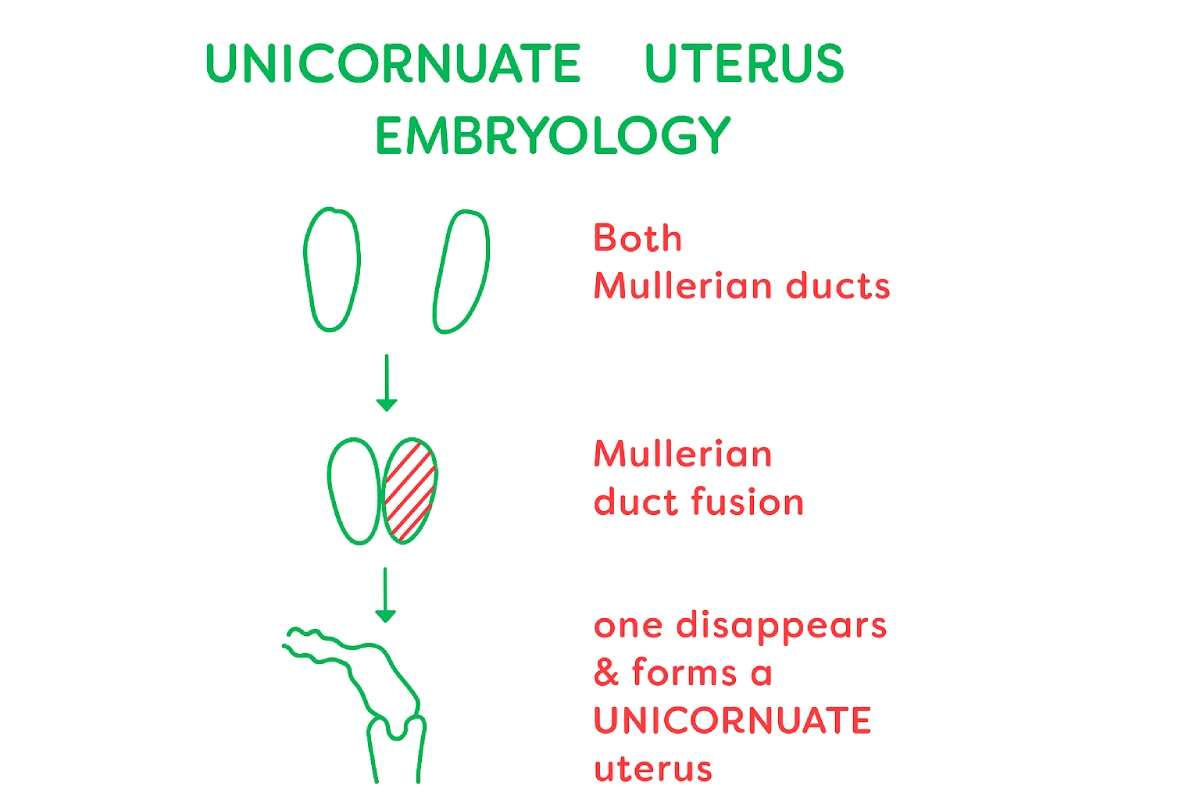
Unicornuate Uterus Embryology – Why Does it Happen?
During the early stages of development (embryology), every female embryo has two Müllerian ducts. These ducts normally grow downward and then fuse together to form a single, complete uterus.
However, if this fusion process does not happen properly, one duct may not develop fully or may even disappear completely. When this happens, only one side of the uterus forms correctly, leading to a condition called a unicornuate uterus.
In some cases, a small piece of the second duct may remain. This leftover piece is called a rudimentary horn, which may or may not be connected to the main uterus.
This variation occurs because of something known as differential canalization—a natural but sometimes faulty process in which the ducts develop and fuse. That’s why some women may have just a unicornuate uterus, while others may also have an additional rudimentary horn.
What are the symptoms of a unicornuate uterus?
Most women with a unicornuate uterus have no obvious symptoms. Symptoms usually appear only when there is an obstructive rudimentary horn:
In every case of Müllerian anomalies, it’s common to have symptoms including pelvic or abdominal pain, menstrual issues, and occasionally endometriosis, which can affect fertility and quality of life.
Whenever the pathology is obstructive, as a result of this, whenever there is an associated rudimentary horn, which is noncommunicating, that can cause a severe amount of pain and endometriosis, and it may be diagnosed very early.
A non-communicating rudimentary horn is typically diagnosed in the age group of fourteen to sixteen years, due to the associated severe pain that it gives rise to.
In the absence of that, the majority of the women who have a unicornuate uterus come to know about it whenever they are trying for a pregnancy.

Get Expert Guidance from Dr. Jay Mehta—Müllerian Anomaly Specialist in India
What are the different types of a unicornuate uterus?
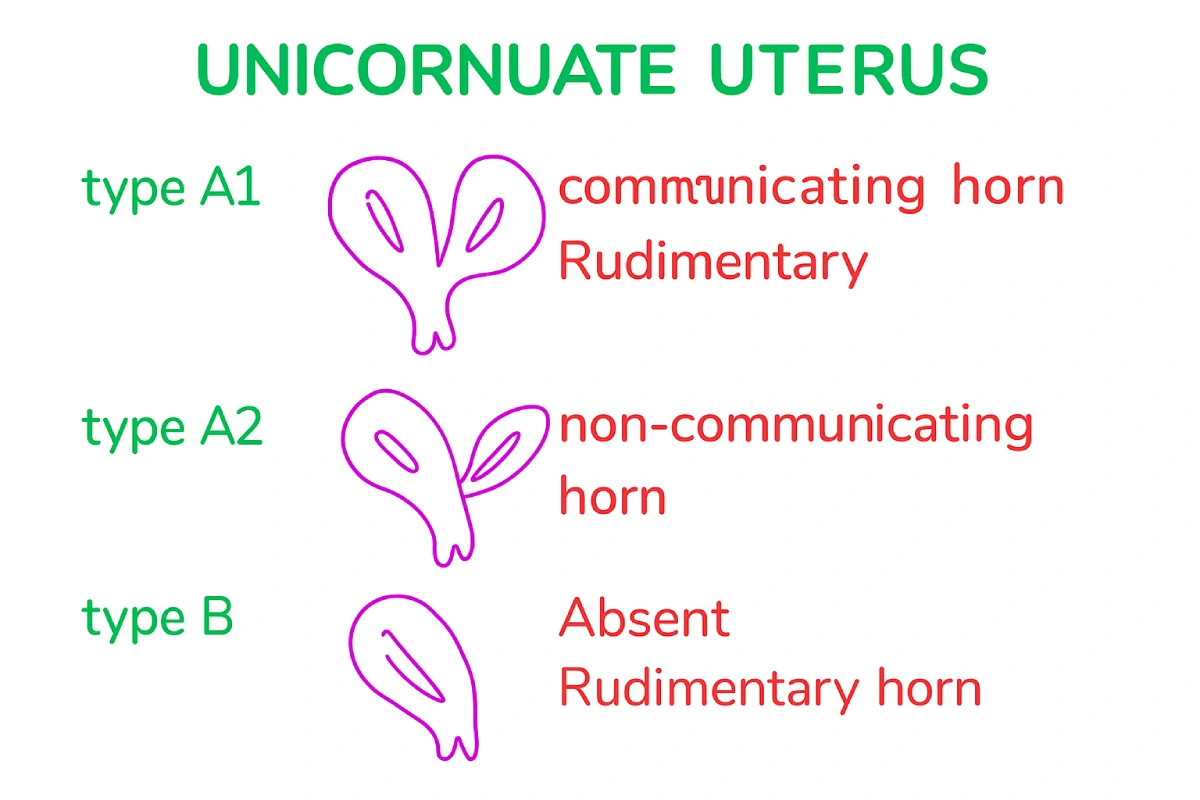
Unicornuate uterus is typically classified into:
1. Non-Communicating Obstructive Horn (The Problem):
- All types of obstructive rudimentary horns (where the endometrial cavity of the horn does not connect to the primary uterus) will almost always be associated with severe abdominal pain and endometriosis.
- In these situations, the patient will almost always require surgical management (laparoscopy) to remove the entire rudimentary horn and prevent further complications.
2. Communicating Horn (No Problem):
If the rudimentary horn is directly connected to the endometrial cavity of the functional Unicornuate Uterus, there is no reason to worry. The patient may or may not require any type of surgical management.
3. Absence of Rudimentary Horn:
If there is an absence of a rudimentary horn, these patients would typically only require a simple office hysteroscopy to assess the main endometrial cavity before attempting conception.
How is a Unicornuate Uterus Diagnosed?
Unicornuate uterus and its associated anomalies are best diagnosed in the form of a 3D ultrasound of the pelvis.
This is going to be the most common ultrasound, which is going to be done for the patient, especially when we suspect any type of Müllerian anomaly.
If you’ve been diagnosed with a unicornuate uterus or are facing difficulties in conceiving, don’t lose hope. At Shree IVF Clinic, Mumbai, I, Dr. Jay Mehta, specialize in managing complex Müllerian anomalies with a focus on fertility preservation and advanced reproductive care.
📞 Book a consultation today at 1800-268-4000 to discuss your case and explore personalized treatment options.
What anomalies are commonly associated with a unicornuate uterus?
A unicornuate uterus is often linked to renal anomalies. These may include:
- Abnormal location of the kidney
- Malpositioned kidney
- Absent kidney (renal agenesis)
This is why we always recommend a kidney evaluation along with a uterine assessment.
One has to realize and understand that no 2 patients are going to be the same when it comes to a particular type of mullerian anomaly. This is precisely because of the differential canalisation and fusion, which occurs across the Müllerian tract, during the phase of embryological development
What are the pregnancy and fertility outcomes in women with a unicornuate uterus?
Because the size of the uterine cavity is greatly reduced, when it comes to a unicornuate uterus, a big problem of this disease is having preterm labor.
Most of the women who have a unicornuate uterus end up having an abortion in the second trimester; also, quite a lot of them have preterm labor. Because only a single side of the fallopian tube is functional, quite a lot of these girls also end up having primary infertility.
Even when these patients undergo Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART), most will eventually need In Vitro Fertilization (IVF). Furthermore, during IVF, we almost always advise transferring an embryo that has been tested and confirmed as chromosomally normal. In these situations, we nearly always recommend transferring only a single embryo at a time.
Success rates with embryo transfer in a unicornuate uterus are approximately 25%.
What pregnancy complications are associated with a unicornuate uterus?
Just like how we’ve mentioned above, when it comes to the aspect of the pregnancy, the majority of the women who have a unicornuate uterus would end up having a cesarean section.
Quite a number of times, the presentation of the baby is going to be in the breech presentation. Careful counselling should be done with the entire family.
When it comes to having a preterm birth for the child, that is one of the most common things that happens in a unicornuate uterus.
This is why careful counselling and close monitoring during pregnancy are essential.
What are the surgical and non-surgical treatment options for a unicornuate uterus?
There is no specific surgical treatment to correct a unicornuate uterus itself. However, treatment focuses on managing associated complications like endometriosis and obstruction.
Nonsurgical options include fertility treatments like IVF and close monitoring during pregnancy.
What is the relationship between a unicornuate uterus and a rudimentary horn?
When we talk about a rudimentary horn in a unicornuate uterus, there are three main possibilities, and each needs to be understood clearly:
1. Obstructive rudimentary horn (not connected to the uterus):
-
- In this type, the horn has its own endometrial cavity but is not connected to the main uterus.
-
- Blood and tissue from periods get trapped inside, which often causes severe abdominal pain and can lead to endometriosis.
-
- In almost all such cases, surgery is required to remove the rudimentary horn completely.
2. Rudimentary horn connected to the uterus:
-
- Here, the horn is directly connected to the main uterine cavity.
-
- Since blood can flow normally, there is no obstruction.
-
- Most women with this type do not face serious problems, and surgery is usually not required.
3. No rudimentary horn present:
-
- In some women, there is no rudimentary horn at all.
-
- In this case, doctors usually only check the uterine cavity lining (endometrium) with a simple test called office hysteroscopy.
-
- No further treatment is typically needed unless other issues are present.
In short, whether a rudimentary horn needs treatment depends on whether it is obstructive or not. Obstructive types almost always require surgery, while connected or absent horns usually don’t cause major issues.
What is the long-term outlook for women with a unicornuate uterus?
With proper diagnosis and management, many women with a unicornuate uterus go on to have successful pregnancies. However, since outcomes vary from patient to patient, personalized treatment and fertility counseling are key.
FAQs About Unicornuate Uterus
– Does a Unicornuate Uterus mean I only have one ovary?
No. The Unicornuate Uterus is a defect of the Müllerian ducts (which form the uterus and tubes), but the ovaries develop separately. You typically have two functioning ovaries.
– Can I get pregnant with a unicornuate uterus?
Yes, but the chances of miscarriage or preterm birth are higher. Many women may need IVF and close pregnancy monitoring.
– Does a unicornuate uterus cause infertility?
Not always, but since only one fallopian tube functions, infertility can occur in some women.
– Will I need surgery to enlarge my uterus?
No. There is no surgical procedure available to safely increase the size of the functional Unicornuate Uterus cavity. Surgery is reserved for removing an obstructive rudimentary horn or treating associated endometriosis.
– Can IVF help women with unicornuate uterus?
Yes. IVF with chromosomally tested embryos improves success rates, though outcomes remain more challenging compared to women with normal uterine anatomy.
Dr Jay Mehta
Scientific Director & IVF Specialist with 10+ years of experience
CALL US 24/7 FOR ANY HELP
GET IN TOUCH ON


