Are Mullerian Anomalies a Problem for Infertility?
UPDATED ON 28TH MAR. 2024
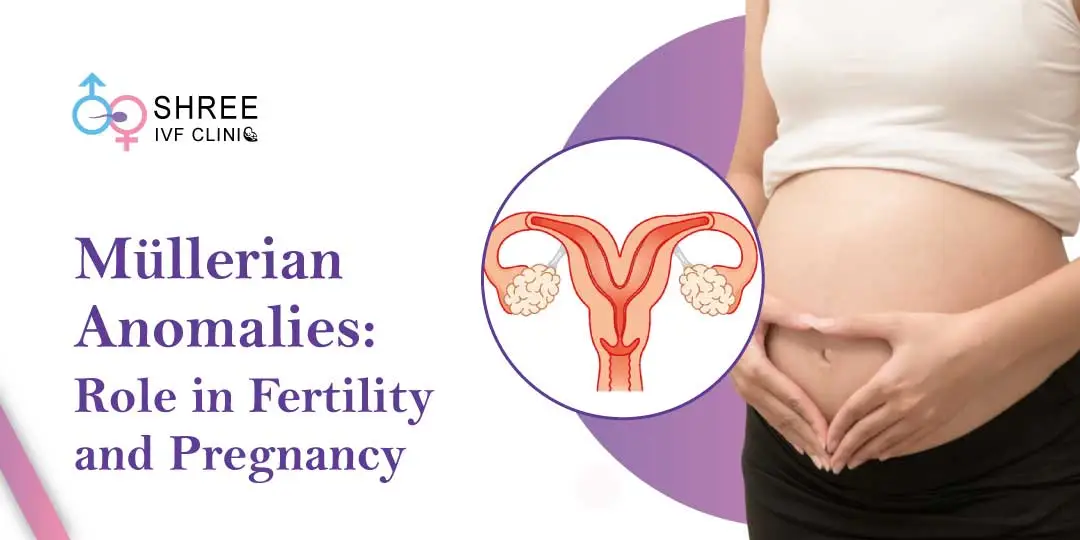
Problems with the female reproductive tract can arise due to Müllerian anomalies, which occur when the Müllerian ducts do not develop or fuse correctly during embryogenesis. From a complete absence of the uterus and vagina (Mayer-Rokitansky-Küster-Hauser syndrome) to more minor anomalies like a bicornuate uterus, these abnormalities can present in various forms.
It’s crucial to grasp the impact of Müllerian anomalies on reproductive anatomy, especially since certain types can have a notable effect on fertility and pregnancy results. When it comes to infertility, recognising and effectively treating these conditions is crucial for both medical professionals and individuals hoping to start a family.
AUTHOR
Dr Jay Mehta
Scientific Director & IVF Specialist with 10+ years of experience
CONDITION
GET IN TOUCH ON
Reproductive Anatomy Overview
The female reproductive system is an intricate network of organs crucial to reproduction. Deep within the body is the uterus, where embryonic growth takes place, surrounded by the fallopian tubes and ovaries that handle the maturation and movement of eggs.
The cervix is the entrance to this system, connecting to the vagina, which is part of the reproductive tract. An essential element in the formation of these structures involves the Müllerian ducts.
As development progresses, these ducts transform to create the upper vagina, uterus, and fallopian tubes, establishing the basic framework for reproductive function in adult women. Proper development of the Müllerian ducts is crucial for establishing a functional reproductive anatomy supporting conception and pregnancy.
Understanding Müllerian Anomalies: Different Types and Underlying Causes
There are different types of Müllerian anomalies, each originating from a distinct embryological cause. Here are some of the most prevalent types:
- Mayer-Rokitansky-Küster-Hauser (MRKH) syndrome: Characterised by an absent or underdeveloped uterus and vagina.
- Unicornuate uterus: Development of only one side of the Müllerian duct, resulting in a uterus with a single horn.
- Bicornuate uterus: Partial fusion of the Müllerian ducts, leading to a heart-shaped uterus.
- Didelphys uterus: Complete non-fusion of the Müllerian ducts, resulting in two separate uterine bodies and cervical canals.
- Septate uterus: Incomplete resorption of the median septum between the ducts, causing the uterus to have a septum down the middle.
- Arcuate uterus: A mild indent at the top of the uterine cavity.
The cause of these anomalies is usually multifactorial, resulting from disruptions in the typical embryological development of the Müllerian ducts. Factors such as genetic predispositions, exposure to environmental teratogens, or maternal health conditions during critical periods of fetal development can play a role. Identifying these structural variations early on is crucial for reproductive health, as they can impact fertility and obstetric outcomes.
Effect on Fertility
The effects of Müllerian anomalies on fertility are significant and diverse.
- For individuals with MRKH syndrome, the lack of a functional uterus makes natural conception unattainable. Nevertheless, assisted reproductive technologies such as surrogacy offer the possibility of having biological children.
- If you have a unicornuate uterus, the smaller size and decreased blood flow can impact implantation and fetal growth, potentially resulting in increased miscarriage and preterm birth rates.
- Women who have a bicornuate or didelphys uterus may encounter difficulties such as a higher likelihood of cervical incompetence, which may necessitate cerclage to support the pregnancy.
- Furthermore, a septate uterus is linked to the highest rates of recurrent pregnancy loss because of inadequate blood supply to the septal tissue, making it less favorable for embryonic development.
- Having surgery to remove the septum can frequently lead to better results.
- Finally, an arcuate uterus generally has a minimal effect on fertility but could slightly increase the chances of pregnancy complications.
It’s crucial to detect these issues early and create personalized treatment plans to improve fertility outcomes for those impacted by these conditions.
Diagnosis and Examination
Detecting Müllerian anomalies primarily depends on non-invasive imaging methods. Ultrasound, particularly the 3D version, is commonly used as the first diagnostic tool because of its accessibility and cost efficiency.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is used for a more thorough evaluation, providing high-quality images that help map out uterine structures accurately.
While laparoscopy is not commonly used for diagnosis because of its invasiveness, it can offer conclusive confirmation of abnormalities and is occasionally combined with hysteroscopy for a thorough assessment of the uterus.
Identifying these issues early on is crucial for effective family planning and reducing the chances of fertility problems and pregnancy complications.
It’s important to get checked out promptly, especially for those looking to start a family soon or young women who want to be prepared for any future reproductive health issues.

4,790+
379K+
” Every individual and couple’s journey is unique, and
finding the right solutions tailored to their specific
circumstances can make all the difference “
Exploring Different Treatment Choices
Treating Müllerian anomalies requires a combination of medical and surgical approaches customised to the particular type and extent of the condition. Treatment may involve hormonal therapy to help regulate menstrual cycles and address symptoms. When it comes to structural anomalies, surgery is frequently the primary treatment option.
Take, for example, a septate uterus, which poses a significant risk of miscarriage and is often treated with hysteroscopic septum resection. This procedure is minimally invasive and aims to restore a more normal uterine shape, increasing the likelihood of carrying a pregnancy to term.
For females with a bicornuate uterus, a more extensive procedure called Strassman Metroplasty may be carried out to connect the two separate uterine cavities. While this method can lower the chances of early delivery, it is usually recommended for women who have experienced pregnancy problems related to this issue.
Every procedure has advantages and disadvantages, and its effect on fertility can vary. Medical procedures are performed to decrease the chances of miscarriage and other issues during pregnancy, ultimately improving the chances of a successful pregnancy.
Patients must have a comprehensive preoperative assessment and discuss in detail with their reproductive specialist the possible results and long-term fertility effects of the selected treatment.
Prevention and Preconception Care
Preventing developmental anomalies is challenging as they usually occur from birth, originating during the early stages of foetal development due to genetic or environmental factors.
Given this, early detection through regular check-ups can be crucial. For people with these conditions, preconception care becomes even more crucial. This level of care involves thorough assessments by experts who can evaluate the uterine structure and provide suggestions to improve fertility results and minimise potential pregnancy complications.
Adjusting your lifestyle, focusing on overall health, and addressing any existing medical issues are important steps in getting ready for a successful pregnancy.
By tailoring care plans to include nutritional guidance, genetic counselling, and emotional assistance, healthcare professionals can assist individuals in managing the challenges of conception and pregnancy when dealing with specific anatomical variations.
Ultimately, Müllerian anomalies pose unique challenges in the field of reproductive medicine. Although it’s not possible to prevent these congenital conditions, early detection and careful management play a crucial role in reducing risks and improving the chances of a successful pregnancy.
Thoroughly assessing the patient before surgery and having open conversations between the patient and the Gynecologist who treats Müllerian duct anomalies set the stage for making well-informed choices about treatment options. Understanding Müllerian anomalies requires a thorough fertility assessment and treatment plan that includes medical interventions, lifestyle changes, preconception care, and tailored support services.
AUTHOR
Dr Jay Mehta
Scientific Director & IVF Specialist with 10+ years of experience
CONDITION
CALL US 24/7 FOR ANY HELP
GET IN TOUCH ON
Share Article on
Recommended Reading
Müllerian Duct Anomalies: Role in Fertility and Pregnancy
Explore Müllerian Duct Anomalies’ impact on fertility and pregnancy. Discover types, diagnostics, treatments, and antenatal care with expert guidance.
Can You Get Pregnant with MRKH?
Curious about pregnancy with MRKH syndrome? Discover fertility options and treatment insights in our comprehensive blog. Learn about the impact of MRKH on conception, diagnostic methods, and the latest reproductive technologies.
What is the difference between MRKH type 1 and type 2?
Distinguish between MRKH Type 1 and Type 2, subtypes of Mayer-Rokitansky-Küster-Hauser syndrome. Explore symptoms, diagnoses, treatments, and the value of multidisciplinary care.